Technical Overview
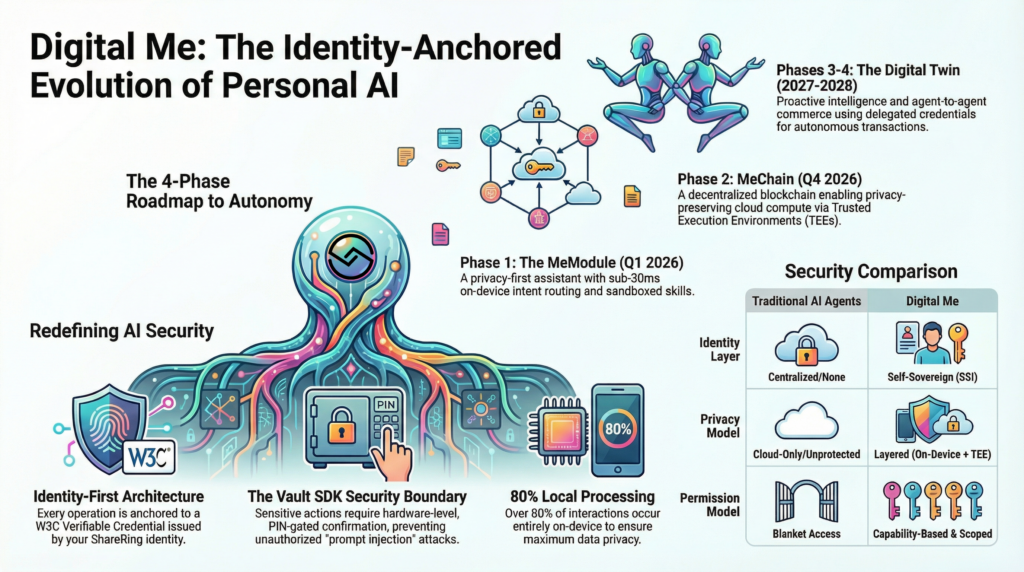
This document provides a comprehensive architectural overview of the ShareRing ecosystem, covering the multi-layered platform stack from the Trust Layer (ShareLedger blockchain) through smart contracts, cross-chain bridges, and applications. It details the global hybrid infrastructure strategy using multiple cloud providers, the Tendermint BFT consensus mechanism, and both built-in Cosmos SDK modules and custom ShareLedger modules (Electoral, Gentlemint, Swap, DistributionX, Fee). The document also explains the Identity and Privacy Engine, including AI-powered verification workflows, ZK-SNARK integration, and the ShareRing DID method. Additionally, it covers cross-chain interoperability with EVM chains and Hedera, and introduces platform components like the ShareRing App vault and ShareRing LINK workflow system for credential verification.
Identity Protocol Specifications
DID and ZKP Specifications/did-method-spec
The SHR DID Method Specification formally defines how decentralized identifiers are created, resolved, updated, and revoked on ShareLedger. Derived from the Ethereum ETHR DID method but adapted for CosmWasm, it uses hex-encoded secp256k1 public keys as identifiers in the format did:shr:<public-key>. The specification details how DID documents are dynamically constructed by querying the CW1056 registry contract and enumerating blockchain events. Key features include zero-cost identity creation (no on-chain transaction required), support for delegate keys and attributes, native versioning through block height queries, and compatibility with W3C DID standards.
DID and ZKP Specifications/cw1056-standard
The CW1056 standard defines the CosmWasm smart contract that serves as the on-chain identity registry for ShareLedger. Derived from Ethereum’s ERC1056, it provides a gas-efficient method for managing keys, delegates, and attributes without bloating on-chain storage.
The contract supports ownership transfers, delegate management with time-based validity, and arbitrary attribute storage. All modifications emit events (did_owner_changed, did_delegate_changed, did_attribute_changed) that DID resolvers use to reconstruct identity documents. The standard also supports meta-transactions through signed messages, enabling third-party gas funding.
DID and ZKP Specifications/zkvct-spec
The ZkVCT (Zero-Knowledge Verifiable Credential Token) specification describes ShareRing’s privacy-preserving credential system built on zk-SNARKs. It enables users to prove identity claims (such as “I am over 18”) without revealing the underlying personal data. The document covers the complete lifecycle: issuance (where credentials are hashed into Merkle trees and anchored on-chain), proving (where users generate Groth16 proofs locally on their mobile device), and verification (where smart contracts validate proofs against trusted Merkle roots). Technical details include the use of the Poseidon hash function, BN254 elliptic curve, nullifiers for preventing correlation and double-spending, and example Circom circuit code for age verification.
Developer Guides
Me Module Developer Guide
This guide provides everything external developers need to build Me Modules, which are web applications that run inside the ShareRing Me mobile app via an embedded WebView. It covers project setup using Vite and React, the required manifest.json configuration, and optional offline mode with zip bundles for low-connectivity scenarios. The bulk of the document is a complete API reference for the message bridge protocol, documenting all available events across categories: Common (app info, device info, storage), Navigation, Vault (document access and queries), Wallet (account management, transaction signing), NFT, Cryptography (encrypt, decrypt, sign, verify), and mobile wallet passes (Google Wallet and Apple Wallet). The guide includes code examples for the bridge helper, transaction creation using @shareledgerjs/client, and best practices for mobile-first design.